Building Insulation: Types, R Values, Benefits

With the rising standard of living, people around the globe are searching for more comfortable lifestyle options. Whether it is a residential, commercial, or industrial building, sustainable building insulation solutions have their demand everywhere.
Building thermal insulation curtail unnecessary energy requirements, offer a suitable indoor temperature, and diminish heat transfer between the different parts of a building and its surroundings. The material also promotes the longevity of building structures, resilient thermal efficiency, and improved energy proficiency.
In this article, we will discuss building insulation types, the different kinds of materials available in the insulation market, the benefits of insulating buildings, and the installation process.
What is Building Insulation?
Building insulation refers to materials installed in a building to minimize the transfer of thermal energy. This is one of the finest ways to fulfill thermal energy requirements and enhance energy productivity for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes. Building insulation materials creates resistance against the movement of heat to keep indoor temperatures favorable in both winters and summers. By reducing thermal energy movement between the interior and exterior of a building, the insulation brings down costs on energy requirements.
The contemporary insulation requirements need sustainable and environment-friendly solutions, and building thermal insulation is the key to the future. According to global estimations, the building insulation market is likely to expand from $29.2 billion in 2023 to $37 billion by 2028. Market analysts also estimated that the market will grow at a rate of 3.3% from the year 2024 to the year 2032. The expected growth is close to a 6% CAGR between 2023 and 2032.
Building insulation types are fundamental to building construction because it curtails heat transfer through walls, ceilings, floors, and other parts of a building to the surroundings. One can choose from a variety of building insulation materials, depending on factors like R-value, sustainability, resistance against moisture, cost, and durability. Various insulation materials, like mineral wool, cellulose, fiberglass, aerogel, spray foam, etc., offer state-of-the-art insulation solutions for effective thermal needs. It helps in controlling indoor temperature, curtails unnecessary energy waste, and brings down energy costs.
How Building Thermal Insulation Works?
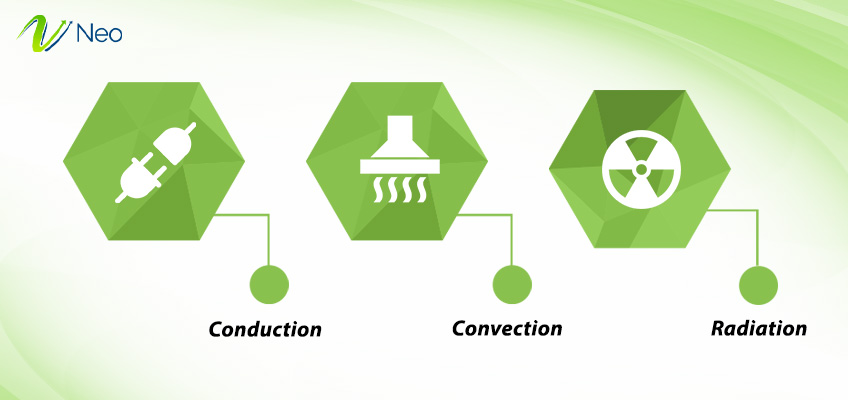
Building insulation work on the simple technique of minimizing heat loss in a cold climate and heat gain in a hot climate. In the first place, it creates a barrier and curtails the movement of heat through conduction, convection, and radiation between the different parts of a building like walls, ceilings, floors, etc., and the atmosphere. Thermal insulation creates small air pockets around the insulated material that act as deterrents against energy movement. In some cases, insulation material can also reflect radiant heat away or use other techniques for better thermal efficiency.
Let’s see how building insulation works and the techniques involved in impeding heat flow:
- Conduction: Materials like fiberglass, mineral wool, foam board, etc. diminish the heat flow through conduction. In conduction, heat transfers from one medium to another through the physical contact of molecules. Here, insulating materials prevent heat flow by trapping air in small air pockets and creating a hindrance in direct contact between the molecules of the two surfaces. Materials create a barrier between the interior and exterior of a building.
- Convection: In convection, heat moves from one medium to another with the movement of fluids or gases. When hot air rises above and cold air sinks down, it generates an air current where air moves from a warmer region to a colder region, carrying heat away. Building thermal insulation materials like cellulose fibers and fiberglass disrupts transfer of heat through convection. They fill up areas like wall cavities, attic spaces, and other areas where movement of air takes place and prevent any heat flow. It prevents the movement of air between the interiors and exteriors of a building.
- Radiation: Radiation involves the transfer of heat without the involvement of any medium in the form of electromagnetic waves. When different parts of a building emit thermal radiation, materials like metallic foil-foam boards reflect radiant heat away from the building. The building thermal insulation acts as a barrier between radiant heat and the insulated surface and reduces heat gain. This method is very useful in areas with a hot climate. Certain insulating materials also have additional coatings for improved performance.
Thermal mass also plays an important factor in building insulation. Thermal mass is the ability of a material to absorb and store thermal energy. Material like concrete or adobe absorbs excessive heat during the day and radiates it out at night. However, it is less effective in comparison to other insulating materials.
Building thermal insulation works on different kinds of mechanisms to ensure effective thermal resistance and barricade heat transfer. In addition to this, thickness of material, density, climate, and specific insulation requirements also play an important role in the working of insulation materials.
Looking For Insulation For Your Building?
Building Insulation Types
There are different kinds of building insulation materials present; each has its own unique characteristics, composition, and advantages.
Here are different types of building thermal insulation materials:
1. Fiberglass Insulation Material
Fiberglass insulation material is known for its economical, effective, and versatile role. It is made up of glass fibers obtained from recycled glass materials. The fibers are bonded with one another using specialized (thermosetting) resin to build an efficient insulating material. Fiberglass is resistant to thermal conductivity because, as air is a poor conductor of heat, it traps air molecules within its matrix and creates small air pockets to diminish heat flow. Insulating material is widely opted for insulation in residential and commercial buildings and has a variety of advantages.
Characteristics of Fiberglass Insulation:
- It is fire-resistant and does not require additional additives.
- It is not useful in excessively hot climates.
- It has R-value from R-2.8 to R-3.5.
- It is non-combustible and does not melt.
Advantages of Fiberglass Insulation:
- It has a high thermal resistance value (R-value).
- It is a durable and versatile material and is easily cast into batts, rolls, sheets, and loose fills.
- It is cost-effective and easy to install.
- It prevents mold and mildew growth.
- It is environment-friendly and sustainable.
2. Mineral Wool Insulation Material
Mineral Wool Insulation is divided into two types. One is rock wool; this material is obtained from minerals like basalt and diabase. The second type is slag wool, which is produced from blast furnace slag obtained from steel mills. The building insulation material is synthesized by melting different raw materials at high temperatures and fanning the molten minerals into fibers.
Characteristics of Mineral Wool Insulation:
- It contains up to 75% of post-industrial recycled material.
- It is a non-flammable material with fire-resistant qualities.
- It has an R-value ranging from R-2.8 to R-3.5.
- It does not melt, and it is non-combustible.
Advantages of Mineral Wool Insulation:
- It is a chemically stable compound and does not degrade over time.
- It can also be used as a sound-absorbing material because it has excellent sound-absorbing properties.
- It offers high thermal resistance and reduces the transfer of heat through the walls, ceiling, and floors of a building.
- It is a durable and flexible material that can be easily drawn into blankets (batts and rolls), loose-fill, blown-in, and fiber insulation.
3. Cellulose Insulation Material
Cellulose insulation is obtained from recycled paper, like newspapers. To manufacture insulating material, first paper is cut into very small pieces, and then, with the help of a chemical, it is fiberized.
Characteristics of Cellulose Insulation:
- It is obtained by adding mineral borate or ammonium sulfate to natural materials to enhance resistance properties.
- It is compact and, therefore, contains no oxygen within it.
- It has thermal resistance (R-value) from R-3.1 to R-3.7.
- It is suitable to minimize fire damage as it inhibits airflow between the surface and the surroundings.
Advantages of Cellulose Insulation:
- It is suitable for both new and existing homes.
- It offers high thermal resistance when placed in open attics or densely packed in cavities (present in walls and ceilings).
- It is fire-retardant and has non-combustible properties.
- It offers efficient air sealing and enhances the building’s air tightness.
- It is environment-friendly as the material used is obtained from recycling (about 82–85%).
4. Polystyrene Insulation Material
Polystyrene insulation material is a product of synthetic and highly processed petrochemicals with fire resistant properties. It can be drawn into a variety of shapes and thicknesses, depending on the requirements. Polystyrene is a colorless and transparent material, and it is used in rigid foam to provide stability.
There are three kinds of polystyrene insulation:
- Molded Expanded Polystyrene (MEPS): It is a versatile material that offers high resistance against moisture and heat. Material can be used as foam boards and small foam beads.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS): It is a lightweight, durable, and strong material suitable for thermal insulation in buildings. It can be easily molded into boards, blocks, or any other shape.
- Extruded Polystyrene (XPS): It has high compressive strength and offers strong resistance against heat movement. It is suitable for low-grade roofing, wall, and ceiling insulation.
Characteristics of Polystyrene Insulation:
- It is available in loose-fill form, concrete block, insulating concrete form, structural insulating panel, and foam board.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) has a thermal resistance (R-value) of R-4, and XEP has an R-value of R-5.5.
- It is prone to thermal drifting and aging.
- It uses material that can accumulate static electricity.
Advantages of Polystyrene Insulation:
- It has excellent waterproof properties.
- It is durable and lightweight.
- It is suitable for both sound and thermal insulation.
- It is easy to install.
5. Natural Insulation Materials
Natural insulation includes different kinds of insulating materials like cotton, sheep’s wool, straw, hemp, and other natural materials.
- Cotton: The cotton insulation material is comprised of recycled cotton and plastic fibers. Out of 100%, 85% is recycled cotton, and the rest, 15%, is fiber. The ingredients in cotton insulation are treated with borate to make them resistant to heat transfer.
- Sheep’s Wool: To add insulation properties to sheep’s wool, it is treated with borate. This treatment with the chemical offers it resistance against fire, pests, and mold. The thermal resistance of sheep’s wool is R-13 and R-19, depending on the different sizes available.
- Straw: For creating insulating material, straw is placed between the layers of Kraft paper on each side. The panels are produced without adding any adhesive, and they are usually 2 to 4 inches thick.
- Hemp: It does not have any special insulation properties. However, its R-value is equivalent to that of fibrous insulation material.
Characteristics of Natural Insulation:
- It is obtained from renewable sources like plants, minerals, and animals.
- It has low embodied energy in comparison to other synthetic insulations.
- It is a non-toxic material and does not emit any harmful gases.
- It has a high thermal mass and stores a high volume of heat.
Advantages of Natural Insulation:
- It has high breathability, which helps it maintain indoor humidity levels.
- It offers high sound and thermal resistance.
- It is made up of biodegradable materials and is environment-friendly.
- It is non-toxic and suitable for residential building insulation.
- It offers pest resistance against rodents and insects.
6. Polyurethane Insulation Material
Polyurethane, also known as PU, is a multifaceted material with high thermal resistivity. The material provides excellent protection against heat transfer between the interior and exterior of a building. Polyurethane is available in two forms, closed-cell foam and open-cell foam. The closed-cell foam consists of high-density molecules filled with non-HCFC gas; this allows the foam to expand properly and enhances its thermal resistivity. The open-cell foams do not have high-density molecules and are only filled with air. The spongy texture of open-cell foams is due to the air present in the material. Other varieties of polyurethane use carbon dioxide gas.
Characteristics of Polyurethane Insulation:
- It contains gas with low conductivity in its molecules.
- It has an R-value of R-6.3 per inch.
- It can be used with a layer of foil and plastic facing to strengthen its longevity.
- It is available in liquid sprayed foam and rigid foam board.
Advantages of Polyurethane Insulation:
- It is a multifaceted material available in rigid foam board, spray foam and foam panels.
- It offers an effective air barrier against heat transfer.
- It has high compressive strength and durability.
- It contains good adhesive properties, allowing it to bond tightly with any kind of substrate.
- It is suitable for both sound and thermal resistivity.
7. Polyisocyanurate Insulation Material
Polyisocyanurate, also known as polyiso, is a thermoset plastic with a closed-cell molecular structure. Many properties of polyiso match those of polyurethane. The material consists of hydrochlorofluorocarbon-free gases to provide it with a foamed structure. Polyiso is prone to thermal drift and aging (with time, gases with low conductivity escape out and the place left is filled by air; this is known as thermal drift). This is the reason why foil and plastic facings are applied to strengthen materials’ life and durability.
Characteristics of Polyisocyanurate:
- It is available in foam board/rigid foam, sprayed foam, laminated insulation panels, and structural insulated panels.
- It has great compatibility with roofing systems, including built-up roofs, single-ply membranes, and modified bitumen systems.
- It is a fire-resistant material that contributes to safety against fire damage.
- It has a closed-cell structure that offers high thermal resistivity.
Advantages of Polyisocyanurate:
- It is lightweight and durable. Makes it easy to install.
- It is a versatile material and is used in a variety of places, like walls, roofs, ceilings, and floors, for thermal insulation.
- It provides resistance against moisture.
- It has a high compressive strength.
Other Types of Building Thermal Insulation
Cementitious Foam:
As it is clear from the name, the main ingredient of this insulation material is cement. The insulation material has non-toxic and fire-resistant properties, which makes it a good fit for building thermal insulation. It is manufactured from the minerals that are extracted from the seawater. The properties of cementitious foam are similar to those of polyurethane foam.
Phenolic Foam:
Phenolic foam is an insulating material that uses air for insulation purposes. The material is now available as “foamed-in-place” in the market. Air is the main ingredient that serves as a foaming agent in the material. It shrinks up to 2% after curing, which makes it unpopular as an insulating material.
Schedule Your Building’s Insulation With Neo Thermal
What is the R Value of Building Insulation?
The “R-value” of building insulation refers to its thermal resistance. It measures the ability of the insulation material to resist the flow of heat. The higher the R-value, the greater the insulating effectiveness. R-values can vary depending on the type and thickness of insulation material used. For example, fiberglass insulation typically has an R-value ranging from R-11 to R-38 per inch of thickness, while other materials like spray foam insulation can have higher R-values per inch. It’s essential to consider the R-value when selecting insulation to ensure it meets the energy efficiency requirements of a building.
Benefits of Building Insulation
There are a variety of benefits of building insulation:
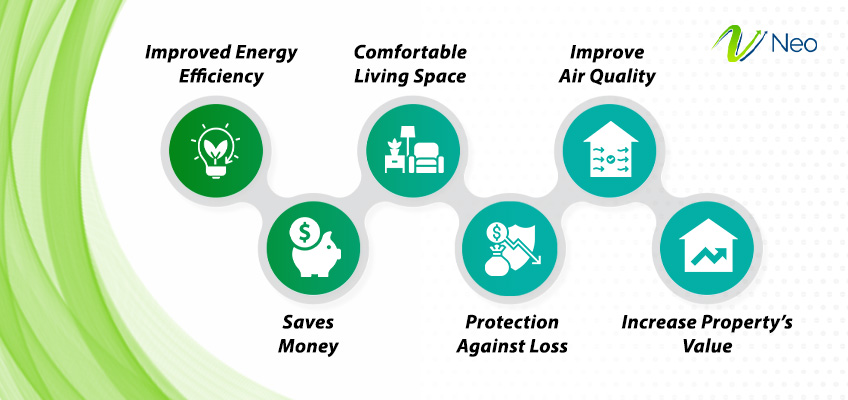
- Improved Energy Efficiency: The first and foremost important benefit of a building thermal insulation materials is enhanced thermal resistance, which results in improved energy efficiency. Thermal insulation helps maintain indoor temperature and curtails excessive load on other electronic appliances by diminishing heat gain and heat loss in summers and winters, respectively. It leads to lower utility costs and energy consumption.
- Saves Money: Unwarranted expenditure on energy always results in money loss. For reducing energy costs and unnecessary spending, building thermal insulation is the best deal. By providing an extra layer of protection against heat loss, thermal insulation will save you money on energy expenses.
- Comfortable living space: It is a fact that residential buildings that are properly insulated will offer a more comfortable living space than those that are not. Insulation protects from fluctuating indoor temperatures, drafts, uneasy spots, and money loss. It offers a happy living space.
- Protection against loss: Insulation materials provide extra strength and life to the building structure. It creates a layer of defense around building materials and prevents structural degradation. Protection against fire, moisture, and condensation improves the life of building materials.
- Improve Air Quality: Building thermal insulation material restricts the infiltration of outdoor dust particles and pollutants. It insulates indoors from any contamination and offers cleaner and healthier air to breathe.
- Increase Property’s Value: A building with high-quality insulation has more market value than a non-insulated one. Insulation offers high thermal and energy efficiency, which attracts potential buyers as it saves them money in the future. Insulation also offers lower utility costs, enhanced comfort, and a sustainable lifestyle.
How to Insulate a Building?
Building Insulation installation is simple; all it requires is proper attention and the right technique to ensure the best performance. Here are the steps you need to follow if you want to attain effective coverage:
- Before beginning insulation installation, analyzing the building’s insulation requirements and preparing an extensive plan is essential. Pay attention to overall size, areas to cover under insulation, climate, personal requirements, and material suitable for insulation.
- It is important to prepare the site where installation is going to be done. Make sure the area does not contain any dirt, debris, or contamination for optimal thermal efficiency. If it is not, first clean the place and secure the work area.
- Based on the analysis done in the first step, choose the right insulation material. Select the material according to your needs, climate, and budget. There are a variety of materials available, like fiberglass, cellulose, mineral wool, polystyrene, and natural materials like cotton, sheep’s wool, straw, etc.
- Take the proper measurement of the area where building insulation material is going to be installed like walls, ceilings, floors, etc. After taking proper measurements, cut the material according to the measured dimensions. Proper measurement ensures effective coverage of the area and the best outcome.
- It is important to install building thermal insulation material according to the industry’s best practices by following the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure placing insulation material between wall studs, ceiling joists, cavities, and gaps on the surfaces and spaces available in attics.
- Additionally, pay attention to air and moisture leakages that hamper the efficiency of the insulating material and the life of the building material. Apply air sealant and moisture-resistant materials around the insulated area.
- Assure that insulation installation must sync with other building systems like HVAC ducts, electric wiring, fire alarm systems, and other important systems. This helps in the prevention of excessive heat loss and heat gain and boosts insulation’s performance.
- Ensure to pay attention to insulation installation guidelines, follow them by heart, take proper quality control measures, and pay attention to proper installation techniques. After installation, a proper inspection must be done to detect any gaps, leakages, or other issues that may affect the thermal insulation.
Points to remember:
- Before applying insulation, it is wise to check the current status of the insulation installation in your building. In some cases, it may be present, but it may get removed because of some electric or construction work. In these cases, you do not need to do any new installation; place it properly.
- If you find any difficulty in installing building thermal insulation, then you must approach the professionals. They will help you with the right insulation solutions and quality work for optimum thermal efficiency.
Proper building thermal insulation installation will not only enhance your energy proficiency but also lead to saving money and energy. It will reduce the extra pressure on your heating and cooling electronic appliances and contribute to more pleasant and stable interior temperatures. You can achieve sustainable environmental goals.
Conclusion
Building Insulation materials are the need of the hour. In this modern era, when humankind requires sustainable and environment-friendly solutions, building thermal insulation materials equips humankind with healthier and more efficient thermal measures. The building thermal insulation not only enhances your comfort level but also offers resilient and sustainable insulation options.
In this article, we provide you with in-depth knowledge of building insulation its materials, types, what they are, and the benefits of installing them. This article helps you make an informed and judicious decision when it comes to insulation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What Materials Are Used for Insulation in Buildings?
There are a variety of building thermal insulation materials available. Each material has its own properties and thermal resistance. Here are the materials:
- Fiberglass
- Mineral Wool
- Cellulose
- Polyurethane
- Polyisocyanurate
- Natural materials like cotton, wool, etc.
2. How To Insulate a Building?
Building insulation process requires proper technique and attention. In this article, we discuss steps to be followed and points to remember while insulating a building.
3. How Can We Construct a Building with Low-Cost Insulation?
For constructing a building with low-cost insulation:
- Select affordable building insulation materials such as fiberglass, mineral wool, cellulose, etc.
- Go for a DIY insulation layer and avoid any air leakage or gaps.
- Search for the government’s incentives and rebates on building insulation installation.
4. What Is the Best Type of Building Thermal Insulation Materials?
There are various kinds of building thermal insulation materials available, such as fiberglass, mineral wool, cellulose, foam board, spray foam, polyurethane, polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, and natural materials like wool or cotton. You can opt for any of these according to your needs and budget. Each material has its own characteristics thermal resistivity (R-value).