Reflective Insulation: A Comprehensive Guide

With rising demands for sustainable and environment-friendly energy requirements, Reflective insulation stands at the forefront. This versatile thermal energy solution is efficient not only for residential building requirements but also for commercial purposes.
There are a variety of insulation options available in the market, however, the solutions offered by reflective foil insulation are unmatchable. If we need to give it a two-word name then it will be “perfect insulation”.
This comprehensive guide on this insulation techniques will let you know about this amazing insulation solution in detail. We will discuss, what is reflective insulation, how it works, different types of materials, and how to install it perfectly.
What is Reflective Insulation?
Reflective insulation, also known as thermal reflective insulation, plays a vital role in cutting down on heat loss and gain between the insulated surface and surroundings and diminishing unnecessary energy requirements. It is the best material to tackle radiant heat with low utility costs.
Reflective house insulation is the combination of highly reflective materials like aluminum or any other metallic foil and substrate materials like polyethylene bubble wrap, foam, or other low-conductivity materials like air. The reflecting surface (metallic foil) is bonded with the substrate material with the help of an adhesive or lamination technique to create a barrier against radiant heat transfer.
Opposite to traditional insulating materials like fiberglass and foam which have an “E” value of more than 0.70, reflective insulating material has an “E” value of 0.03. Its primary goal is to curtail radiant heat transfer by reflecting away heat when positioned against the heat source in contrast with old methods of slowing down conducive heat for insulation. It is more a comprehensive and effective method of insulation, particularly in the areas where climate is extreme.
Reflective Insulation: How Does It Work?
Reflective insulation is one of the most valuable materials for sustainable thermal insulation solutions. The prime objective of the insulating material is to curtail heat transfer emitted in the form of electromagnetic waves between the object and its surroundings. It is not like traditional insulation techniques that focus on slowing down conductive heat transfer. In its true sense, it is a treasure for viable insulation practices.
Transfer of heat between an object and its surroundings takes place in three ways:
- Conduction: When heat transfers from a hot object to its surroundings through physical contact, this is known as conduction. Here, thermal energy requires a medium (solid or fluid) to flow from a hot surface to cool. Example: transfer of heat from the hot exterior walls of a house to the interiors.
- Convention: When air moves from high density to low density, convention takes place. Under this, the transfer of heat takes place with the help of physical air movement. When hot air rises, cool air rushes to take its place. Example: rising air from the chimneys of industrial plants and homes.
- Radiation: When the transfer of heat takes place through space and a vacuum, it is known as radiation. Infrared rays move from one medium to another without the help of any medium or material. Example: the sun’s energy reaches the earth and is absorbed by the earth’s atmosphere.
Radiant barrier insulation manages the flow of radiant heat between the surface of an object and its surroundings. It uses highly reflective material, such as aluminum or any other metallic foil, to reflect away radiant heat when it strikes the reflective surface and prevents it from penetrating through the insulated surface.
Additionally, this insulation comprises a layer of air bubbles sandwiched between the layers of metallic foil (commonly, aluminum foil) to strengthen insulating properties or low-conductivity material to create a hindrance for heat transfer through conduction or convention.
Radiant barrier insulation works best when it is placed perpendicular to the radiant heat striking the surface. Furthermore, heat reflective sheets provides greater results when the temperature difference between the sides of the reflective material is higher.
Beat the Heat and Cold with Reflective Insulation
Types of Reflective Insulation Materials
There are different types of reflective insulation present to fulfill all kinds of application and installation prerequisites. The major types include:
1. Reflective Foil Insulation:
Reflective foil insulation is the best fit to enhance energy productivity and thermal amenity. It comprises a layer of aluminum foil or a metallic film stratified with foundation material like polyethylene bubble wrap. This foundation material may vary from bubble wrap, or foam to any other low-conductivity material to provide greater resistance. The lamination technique or adhesive is typically utilized to bond the foundation material with aluminum foil or metallic film.
The reflective foil insulation curtails heat transfer between the surfaces it applied and the surroundings. The insulation material has a layer of reflective foil that diminishes heat by reflecting radiant heat dexterously. When installed properly, it creates an obstruction and prevents radiant heat from penetrating through surfaces like walls and roofs. The reflective surface creates an envelope to keep radiant heat away from the applied surface.
Reflective foil insulation applications:
- Use in attics, walls, floors, and clamber spaces present in residential buildings.
- Use in the roofs, walls, and HAVC ducts of commercial buildings.
- Use in the agriculture sector and transportation.
- Use in industrial establishments where managing heat transfer is fundamental.
Reflective foil insulation advantages:
- It has high-grade reflectivity.
- It is lightweight, malleable, and soft.
- It provides resistance against moisture and condensation.
- It is more durable and environment-friendly than any other insulation material.
- It is readily available and affordable and offers long-term energy savings.
2. Radiant Barrier Insulation:
Radiant barrier insulation is composed of highly reflective material for effective insulation, it reduces radiant heat transfer between the insulated material and surroundings. The insulation material is made of metals like aluminum and substrate materials like kraft paper or plastic film, efficiently joined to create a substance that easily keeps radiant heat distant from the insulated material.
The radiant barrier insulation is not like other insulating materials that work on the principle of slowing down conductive heat transfer. This substance is more competent as it reflects radiant heat away. When applied, it prevents heat from entering walls, roofs, or attics and curtails heat gain and loss.
Radiant barrier insulation applications:
- Use in an area with a hot climate where excessive heat gain is a primary concern.
- Use in attic insulation and roof covering.
- Use in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
- Use for providing underfloor insulation.
Radiant barrier insulation advantages:
- It has high reflective properties and is lightweight.
- It is very easy to install, flexible, and durable.
- It offers potent resistance against moisture and condensation.
- It is effective in maintaining a consistent indoor temperature by reflecting heat away.
3. Reflective Bubble Insulation:
Reflective Bubble Insulation retrenches heat transfer with the help of a layer of air bubbles sandwiched between the two reflective foil surfaces. The two outer layers of the insulating material are reflecting foil (made up of aluminum) with a layer of air bubbles trapped between the two surfaces. It increases the thermal efficiency of an object several times and reflects radiant heat ingeniously.
The principle of conduction and reflection is used in the air bubble insulation technique. The material, on the one hand, creates a barrier against conducive heat transfer and on the other hand, it reflects radiant heat away from the insulated object. This combination is efficient for minimizing heat gain and loss at the same time.
Reflective bubble insulation applications:
- Use in HVAC duct insulation, attic insulation, and wall insulation
- Use in transportation like insulating vehicles and containers.
- Use in residential, industrial, and commercial buildings.
Reflective bubble advantages:
- It is lightweight and flexible.
- It has high reflectivity and durability.
- It is easy to install and strengthens thermal resistivity.
- It resists any kind of moisture or condensation.
4. Reflective Foam Board Insulation:
Reflective insulation foam infuses the thermal properties of a foam board with the reflective properties of a metal (like aluminum foil). The insulation foam has a rigid foam board core made of materials like expanded polystyrene (EPS), polyisocyanurate (polyiso), etc. that is placed between the layers of reflective foils. This board acts against conductive heat transfer, and at the same time, reflective foil reflects the heat.
Reflective foam insulation offers protection against both conducive heat and radiant heat. It curtails the conducive heat by entrapping air within the layers of its structure and, concurrently, reflecting radiant heat with the help of reflective foils. The insulation foam strengthens the insulating properties of an object by providing it with a 360-degree cover.
Reflective foam insulation applications:
- Use for roof insulation, underfloor insulation, and wall insulation.
- Use as sheathing for exterior walls.
- Use in HVAC ducts where thermal insulation is necessary.
- Use both in residential as well as commercial buildings.
Reflective foam insulation advantages:
- It has high-insulating properties.
- It is lightweight, rigid, and durable.
- It is very easy to install and offers high thermal insulation.
- It is efficient at resisting moisture.
Protect your Home from Temperature Extremes with Reflective Insulation
5. Reflective Insulating paints or coatings:
Reflective insulating paints or coatings are an amalgamation of acrylic or elastomeric polymers efficaciously infused with ceramic microspheres or other highly reflective materials. It is an innovative way to offer thermal resistance with towering reflectivity. The mixture of reflective particles with paint enhances the paint’s ability to reflect away more heat.
When reflective insulating paints or coatings are applied to the surface of an object, they create an imaginary covering around it to cut down on heat absorption from the surroundings. It keeps the surface cool and lowers the indoor temperature of an object with increased energy efficiency. This type of insulation is much more effective than the traditional foam or fiberglass technique because the combination of reflective particles and paint offers a high degree of thermal insulation through a coating and results in overall energy savings.
Reflective insulating paints and coatings application:
- Use in HAVC ducts, walls, ceilings, and even roofs.
- Use to apply by using techniques like brushing, spraying, or rolling.
- Use in livestock centers and greenhouses.
- Use in refrigerated containers for transportation.
- Use for equipment, machinery, storage tanks, and pipelines.
Reflective insulating paints and coatings advantages:
- It helps with energy savings, by lowering the cost of keeping objects cooler in a hot climate.
- It offers a comfortable indoor temperature by keeping the surface cooler.
- It creates resistance against UV rays.
- It lowers carbon emissions and promotes environmental protection.
6. Reflective Fabric Insulation:
Reflective fabric insulation comprises fabric materials like polyester or nylon laminated with reflective metallic foil such as aluminum foil. It is a specialized material with the reflective properties of metals and the insulating properties of synthetic fabrics. In some cases, the insulation material has supplement layers for additional insulation and moisture resistance.
The principles of conduction and convection are the main driving forces behind reflective fabric insulation. The material reflects a large amount of the sun’s energy and prevents it from entering the object and raising the temperature. The fabric offers an extra layer of protection by trapping air and slowing down the transfer of heat between the surroundings and the object.
Reflective fabric insulation applications:
- Use in residential buildings on walls, ceilings, and floors.
- Use in commercial and industrial buildings to enhance thermal efficiency.
- Used in HVAC ducts and prevents heat absorption.
- Use in spacecraft and satellites to protect sensitive equipment from temperature fluctuations.
- Use thermal blankets to maintain the body temperature of a patient during medical procedures.
Reflective fabric insulation advantages:
- It is lightweight, flexible, and easy to handle and install.
- It is durable and resistant to any type of wear and tear.
- It is environment-friendly and suitable for long-term use.
- It provides resistance against moisture.
- It is highly reflective and efficiently reflects radiant heat. Benefits of Using Reflective House Insulation in Your Homes
Application:
- Reflective foam insulation has several useful applications:
- Use in wall insulation, roof insulation, and underfloor insulation.
- Use in sheathing for exterior coverings.
- Use in HVAC ductwork.
- Use in residential and commercial buildings.
How to Use Reflective Insulation?
Reflective insulation increases energy efficiency and fulfills thermal requirements with low operating and installation costs. It offers structural stability and sustainability.
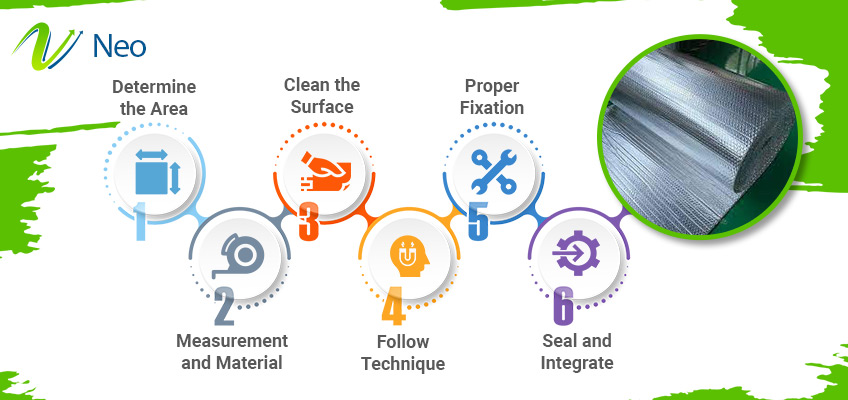
- Determine the area: Before applying reflective insulation, determine the area of your commercial, industrial, or residential building for potent radiant heat reflection like attics, roofs, walls, HAVC ducts, etc.
- Measurement and Material: Do a thorough assessment of the required area where the radiant heat barrier is going to be installed. This thorough assessment will help in procuring the right quantity of material for the best output.
- Clean the surface: It is necessary to clean the surface minutely before putting in insulation material. Make sure to dry, clean, and remove any kind of obstruction, containment, or dust particles for optimal adhesion and results.
- Follow technique: Proper installation techniques must be followed to mitigate radiant heat transfer between the surface and surroundings. Precision in cutting the material, fitting, and covering the required surface is essential.
- Proper Fixation: It is important to imply proper fixation methods for the firm affixing of insulation material to the surface. Use staples, nails, and adhesive properly to avoid any gaps and misalignments that hamper effectiveness.
- Seal and Integrate: Proper sealing and integration methods should be followed to create a perfect barrier against radiant heat. Every joint, gap, seam, and edge must be properly covered using insulation tapes or other compatible materials.
Apart from the above-mentioned steps, it is necessary to accurately determine the climate and environmental conditions of the area where reflective insulation is going to be installed. Regions where the temperature is high and the climate is hot have this insulation that curtails heat gain by reflecting radiant heat away from the surface. On the contrary, in cold climates with low temperatures, thermal insulation prevents radiant heat loss from inside to improve thermal efficiency and reduce heat loss.
Additionally, put a vapor barrier before placing insulating material on the surface in a climate of high humidity. The vapor barrier stops moisture accumulation on the insulated surface. Humidity in the air creates a hindrance to effective thermal insulation.
Don’t let heat or cold disrupt your comfort Install Reflective Insulation Now
Where to Use Reflective Insulation?
Thermal reflective insulation has a variety of applications, from attics to walls, as well as floors and HVAC ducts. This insulation material offers versatile solutions. It is efficiently used in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings to create a blockade against radiant heat transfer and reduce energy consumption. It is lightweight, flexible, and easy to install, making it a sustainable solution for thermal insulation requirements.
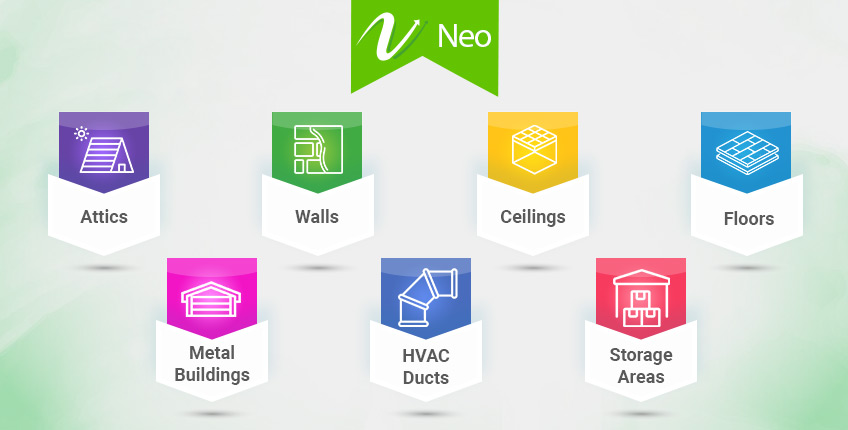
It can be judiciously used in various places to increase thermal efficiency:
- Attics: The attic in our home is the place that is in direct contact with the outside. This insulation creates a blockade and prevents radiant heat from entering during the summer and escaping during the winter.
- Walls: reflective thermal insulation can be easily used on walls as well. It is important to cover walls because a large amount of heat escapes through walls. It helps you attain desired thermal insulation and control temperature fluctuations, saving you money on monthly bills.
- Ceilings: Uncovered ceilings can become a black sheep, helping heat escape rooms faster than you think. It is highly advisable to insulate ceilings with thermal reflective insulation material to maintain a consistent temperature.
- Floors: A lot of heat is lost through the floor. If you overlook this area, it will cost a very high price. Floor insulation is essential not only to get the desired temperature but also to reduce energy consumption costs.
- Metal buildings: It is really important to insulate metal buildings like warehouses, barns, and other industrial facilities to curtail radiant heat transfer and maintain temperatures.
- HVAC Ducts: In many cases, HVAC ducts become an easy path for heat energy loss and gain during the air distribution process. Insulating HVAC ducts ensures efficient heating and cooling, which leads to less energy consumption and lower utility costs.
- Storage Areas: In certain industrial establishments, it is necessary to maintain temperature and protect materials from heat fluctuation. Reflective insulation is one of the best ways to protect these temperature-sensitive products.
How to Install Reflective Insulation?
Proper technique and attention are necessary when it comes to installing reflective insulation in a building. The right approach helps to obtain ideal performance and efficiency.
Here are the steps to keep in mind for installing it
- Clean the area: Before applying this insulation to the surface, it is essential to clean it properly. Any kind of dust particle, debris, or other obstruction must be removed.
- Measurement: Taking proper measurements before installing thermal insulation will ensure proper covering of the desired area and lead to the best results. Make sure to take into account any gap, obstruction, or protrusion that needs adjustment.
- Employing the Right Technique: For reflective foil rolls: Unfold the thermal reflective insulation foil and put it flat over the required place. Remember to place it facing the direction of heat flow. Use tape, staples, or adhesive to fix it properly. Fit it without any wrinkles.
- For reflective foil batts or panels: Put the batts or panels against the desired surface and ensure that they will fit perfectly and without any gaps. Use adhesive, staples, or nails to ensure proper fitting. These rolls, batts, and panels are effective, particularly in hot climates where dealing with radiant heat is the primary concern.
- Seal joints and edges: Create an airtight barrier against radiant heat to get optimum insulation. Do not forget to properly seal every joint, gap, and edge with insulation tape.
Attic Installation:
- To do proper attic installation, put insulation material between the attic joists, ensure complete covering, and avoid any compressions. For securing insulation, place the material with the help of staples or any support.
- To get maximum effectiveness and cover a larger area, place a second layer of reflective insulation at 90 degrees (perpendicular) to the first layer.
Roof Installation:
- To do the roof installation, put the insulation material under the roof rafters and ensure that the reflective surface of the material faces the attic.
- Do not forget to leave a gap between the insulation covering and the roof sheathing this will allow proper ventilation and resist moisture.
Wall and Ceiling Installation:
- For the best outcome, place this insulation material between the wall studs or ceiling joists. Secure the insulation with staples, nails, or adhesive for a tight fit and complete coverage.
- Put in supplementary insulation material if it is required to fill up gaps, cavities, or any other opening.
For installing a foil-type barrier, ensure that the insulating material droops between the attachment points and has an air gap of 1.0 inches between the material and the roof.
Please do not forget to monitor the installed insulating material at regular intervals. It will save you not only from consumption costs but also from any severe damage and deterioration and provide a longer life to the material.
Conclusion
reflective house insulation will offer you an all-round solution for thermal energy requirements. It is one of the most effective ways to get sustainable building practices and conserve energy. In this article, we provide you with a comprehensive guide on reflective insulation, after understanding what is this, how it works, different types, and installation processes, one can make an informed decision that is crucial for one’s energy needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is reflective insulation good for walls?
Reflective insulation is perfectly suitable for walls. It will help to maintain thermal insulation with improved energy efficiency and lower utility costs.
2. How thick is Reflective insulation?
The thickness of thermal insulating material may vary from a fraction of an inch to several inches. The thickness depends upon the application of the product and the space available. The thicker the material higher the insulation.
3. How long does reflective insulation last?
The life of reflective insulation material depends upon factors like the quality of material used, technique used during installation, climate conditions, and regular monitoring. If attention is paid to these details the insulation will sustain for a longer period with low operational costs.
4. Does Reflective insulation require maintenance?
This insulation requires very low maintenance. If properly installed it will function efficiently without any disturbance. However, periodic inspection is necessary to avoid any unnecessary damage. Regular monitoring helps in dealing with wear and tear that may affect functioning.
5. Is reflective insulation effective in all climates?
Yes, it is effective in all climates. In a hot climate, it reflects the radiant heat away from the surface of the insulated object. In cold climates, it curtails heat loss by creating a barrier for radiant heat to escape interior space.