There are many things to take care of to keep your home warm and cozy. First and foremost, a home must have a building envelope with a proper list of thermal insulation materials. Fun fact, you can drastically reduce the energy you use to maintain the home’s climate by reducing heat transfer via the building envelope. Thermal insulation not only prohibits heat transfer but also keeps the sound under control. So, here is a best thermal insulation materials list that are put together that keep your home warmer.
Numerous budget-friendly thermal insulation materials list currently accessible in the market, each varying in cost, R-values, application methods, and environmental effects. Insulating insulation materials in your homes mitigates winter cold losses and summer heat gains, fostering consistent indoor temperatures.
What is Insulation Thermal Material?
Insulation materials play a crucial role in thermal insulation, aiming to minimize heat transfer between objects. Heat transfer poses challenges across various industries when objects in contact have disparate temperatures. Although heat flow between these objects is inevitable, the use of insulation materials becomes instrumental in curbing the transfer. These materials function by diminishing thermal conduction or redirecting thermal radiation rather than absorbing it.
One common type of thermal insulation material is fiberglass, which is composed of fine glass fibers. Fiberglass insulation effectively traps air, creating a barrier that hinders heat conduction. Another widely used material is foam insulation, available in various forms such as expanded polystyrene (EPS), extruded polystyrene (XPS), and polyurethane foam. These materials boast low thermal conductivity and are often utilized in construction to insulate walls, roofs, and floors.
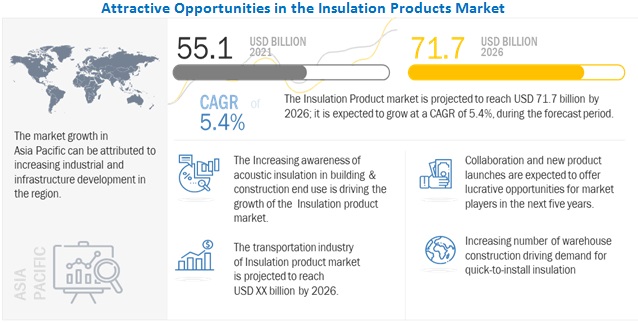
Market Report of Thermal Insulation Materials List
The insulation industry has experienced significant growth in recent years, with market dynamics shaped by factors such as increasing awareness of energy conservation, stringent building codes, and a rising focus on sustainable construction practices. In 2021, the market value of insulation products worldwide reached a noteworthy USD 55.1 billion, and industry analysts project a steady climb to USD 71.7 billion by 2026, representing a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% over the forecast period.
List of the Top 5 Thermal Insulation Materials
When it comes to list of thermal insulation materials, there is a multitude of affordable and widely used materials available in the market. There are various affordable and widely used insulation materials you can find in the market. Many of these have been in use for a long time.
Each insulation material has its pros and cons. So, when choosing the right insulation for your needs, it’s important to know which one suits your situation best. We’ve taken into account factors like R-value (thermal resistance), cost, environmental impact, flammability, sound insulation, and more. Here are the five most commonly used types of insulation materials:
| Insulation Material | Price / sq. ft. | R-Value / in | Environmentally friendly? | Notes |
| Cellulose Insulation | 165/kg | R-3.7 | Yes | Contains the highest amount of recycled content |
| Fiberglass Insulation | Rs 20/sq. ft. | R-3.1 | Yes | Does not absorb water. |
| Mineral Wool Insulation | 21/Kg | R-4 | Yes | Does not melt or support combustion. |
| Polystyrene (EPS) Insulation | 250/square meter | R-4 | No | Difficult to use around imperfections. |
| Reflective Insulation | 1,000 INR | R-3 | Yes | Providing an effective barrier against heat transfer in spaces such as attics and roofs. |
Best 10+ List of Thermal Insulation Materials in 2024
Exploring the list of thermal insulation materials currently available in the market reveals a range of options with varying pricing, R-values, applications, and environmental impacts. Introducing thermal insulation to your home not only stabilizes indoor temperatures by minimizing winter heat losses and summer heat gains but also has the potential to slash your energy expenses by up to half! Here’s a compiled list of the seven most prevalent insulation materials frequently utilized in residential and commercial applications:
1. Cellulose Insulation
Cellulose is quite combustible because it mainly consists of shredded newspaper. You can find cellulose insulation on the ceiling, walls, and attics of your house. Please note that cellulose insulation is not fireproof, even though people treat it with flame retardants.
Furthermore, it retains and absorbs moisture. You can apply cellulose insulation using many ways, out of which you can add water into it. Another point to note here is that cellulose insulation requires the same quantity of untouched materials, such as fiberglass insulation. The only difference is that cellulose insulation needs to triple the cellulose to obtain equivalent efficiency.
Composition: Crafted from recycled cardboard, paper, and similar materials.
R-Value: Ranges from R-3.1 to R-3.7.
Environmental Impact: Considered eco-friendly due to the use of recycled materials.
Form: Typically available in loose form.
2. Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation, found in various structural components such as walls, air ducts, floors, and pipes, is composed of two main subtypes: fiberglass loose-fill and blanket insulation. The loose-fill variety is blown into spaces, while the blanket insulation is available in rolls with varying densities and dimensions. Comprising recycled glass and sand, fiberglass insulation is inherently non-combustible. Other list of thermal insulation materials may include foam board, cellulose, rock wool, and spray foam.
Using fiberglass insulation can be beneficial to you because it can drastically reduce your utility bills and energy usage. It has impressive environmental benefits as it helps reduce fossil fuel combustion to heat and cool buildings. All in all, it reduces the overall carbon dioxide emission.
Composition: Made from recycled glass and sand; naturally non-combustible
R-Value: Effective in minimizing heat transfer.
Environmental Impact: Reduces fossil fuel combustion for building heating and cooling
Form: Comes in rolls with varying densities and dimensions.
3. Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
EPS consists of the fusion of plastic beads of a small size and consists best in the list of Thermal insulation materials. You can notice the use of EPS in concrete tiles. On the other hand, molded EPS comes in small-sized foam beads, and it is widely used for foam board insulation. The only thing you have to take care of is that a tiny hole in the wall or a rush of wind can disperse all the beads.
Polystyrene, a waterproof thermoplastic foam, excels in sound and temperature insulation. It’s available in two types: expanded (EPS) and extruded (XEPS or Styrofoam), differing in performance and cost.
Composition: Composed of expanded polystyrene beads, derived from styrene monomers.
R-Value: Exhibits a moderate to high R-value, providing effective insulation.
Environmental Impact: Production may involve the use of chemicals; recycling is possible.
Form: EPS boards: Available in rigid board form.
4. Extruded Polystyrene
The production method sets extruded polystyrene (XPS) apart from expanded polystyrene (EPS), as covered in the preceding section. XPS originates as a molten substance, molded into sheets. Primarily employed as foam board insulation, XPS also finds application in various general or specialized uses.
Extruded polystyrene differs from expanded polystyrene in various ways. It is in molten form, which is later turned into sheets. You can use it for general purposes, but its primary use is for insulating the foam board. A few of its main advantages are that it is resistant to corrosion, moisture, and rotting. Furthermore, it also has air emission benefits with net-positive energy conservation. Extruded polystyrene (XEPS) distinguishes itself from expanded polystyrene through its molten form, later crafted into sheets. While suitable for general applications, its predominant use lies in insulating foam boards.
Composition: Molten polystyrene transformed into sheets.
R-Value: Typically higher R-value, with specific rating variations.
Environmental Impact: Resistant to corrosion, moisture, and rotting.
Form: Mainly used in insulating foam board; versatile for general purposes
Read Also: Building Insulation: Types, R Values, Benefits
5. Spray Polyurethane Foam (SPF)
in The List of Thermal insulation materials spray Polyurethane Foam is the best material of insulation. SPF is an insulating foam plastic. Spray polyurethane foam is sprinkled as a liquid that dilates multifold. Not only does it provide an air barrier and moisture control, but it also provides a high R-value. This list of insulation materials can also be transformed into roofing foam with durability against foot traffic and water.
Spray polyurethane foam serves not only as an air barrier and moisture control method but also boasts substantial R-value levels. It is widely used to insulate ceilings, roofings, air barriers, attics, and basements. It enhances the environment of your home’s ventilation for efficient functioning and keep room warm in winter.The two main types, open-cell and closed-cell, offer distinct advantages, catering to specific needs and preferences. Overall, spray foam is recognized as one of the best materials for thermal insulation.
Composition: Polyurethane or other materials in liquid form; expands and hardens.
R-Value: TOffers effective thermal insulation with specific R-values.
Environmental Impact: Superior ability to seal air leaks and prevent water leaks.
Form: Available in two main types: Open-cell and Closed-cell.
6. Reflective Insulation
Reflective foil insulation, incorporating an aluminum or similar reflective surface, offers versatility in construction projects. This type of insulation allows for the initiation of certain internal trades before applying tiles and cladding, enhancing on-site workflow efficiency. On its own, reflective foil insulation boasts a modest R-value of approximately R1.0.
However, when correctly installed with a dead air space (sealed cavity with no air movement), significantly higher R-values can be achieved. Suitable for both commercial and residential applications, examples of reflective foil insulation include the Kingspan air-cell range and Fletcher sisalation range, making it a valuable addition to the list of thermal insulation materials.
Composition: Features a reflective surface of aluminum or similar material.
R-Value: On its own, has a modest R-value of around R1.0.
Environmental Impact: Consideration for environmental impact due to material composition.
Form: Flexible and adaptable, allowing for easy installation in various settings.
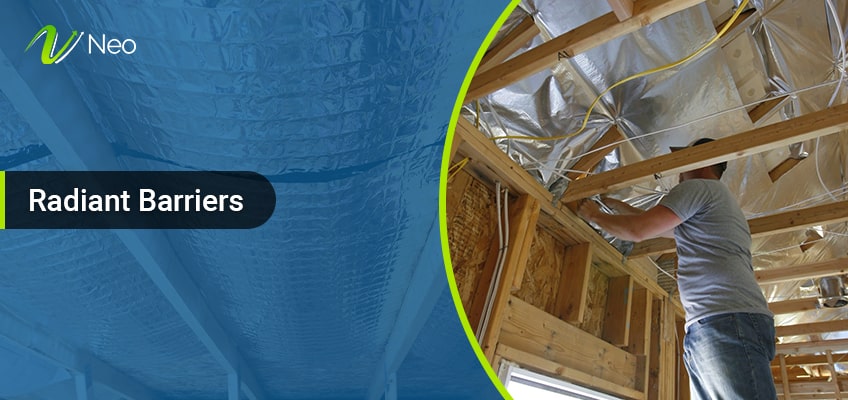
7. Radiant Barriers
Radiant barriers are commonly installed in attics, primarily designed to minimize heat gain in hot conditions, typically during summer, and reduce heat loss in cold conditions, typically in winter. Professionals usually install these thermal insulation materials with the reflective side facing an open-air space. The radiant heat moves away from the body, heating every solid it encounters by absorbing energy. This phenomenon is why the sun heats your roof. Moreover, it contributes to lowering energy costs by blocking approximately 90% of the heat that strikes the surface.
Composition: Typically composed of reflective materials, such as aluminum foil.
R-Value: Low R-value, as it primarily focuses on reflecting radiant heat.
Environmental Impact: Consideration for environmental impact due to material composition.
Form: Thin and lightweight sheets, designed for easy installation in attics.
8. Cotton Insulation
In the list of Thermal Insulation Materials Cotton insulation, crafted from recycled blue jeans, showcases the versatility of repurposing denim. Beyond its environmental and hygienic safety, it excels in sound absorption compared to alternative insulation methods. Installers can work without special safety precautions, eliminating the need for masks or additional equipment. Moreover, it effectively retains its R-value during the winter season. The installation process for cotton insulation mirrors that of fiberglass, providing a familiar approach for installers.
Composition: Crafted from recycled jeans, providing an eco-friendly alternative.
R-Value: Effective R-value, comparable to traditional insulation methods.
Environmental Impact: Environmentally and hygienically safe, promotes recycling.
Form: Available in batts or loose-fill, resembling traditional insulation.
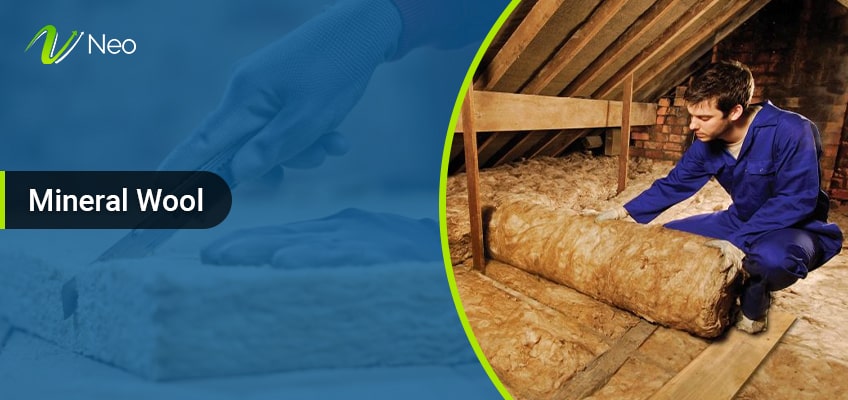
9. Mineral Wool
Similar to fiberglass insulation, mineral wool is available in both loose-fill and blanket forms. Comprising approximately 75% post-industrial recycled content, mineral wool boasts flame resistance without the need for additional chemicals. Rock wool, a synthetic material, incorporates natural minerals, while slag wool is derived from blast furnace slag residue, making it a synthetic insulation material.
Composition: Around 75% post-industrial recycled content; flame-resistant.
R-Value: Varies with specific product; generally competitive with fiberglass.
Environmental Impact: Considerable use of recycled content; reduced need for additional chemicals.
Form: Available in loose-fill and blanket forms.
10. Polyisocyanurate Insulation
This list of thermal insulation materials comprises plastic with closed-cell foam. It also has cells with a low-conductivity gas that provides a decent R-value. But, gas leaks can happen, which let the air inside, lowering the R-value. The insulation comes in liquid foam, rigid foam board, and spray foam. You can also laminate into insulation panels with various facings. In-place foam applications are a better option than installing a foam board because it is more pocket-friendly.
It also has better performance because the liquid foam molds well to the surfaces. Polyisocyanurate insulation, often referred to as polyiso, is a versatile and widely used thermal insulation material. It belongs to the family of rigid foam board insulations and is renowned for its high R-value, making it an efficient choice for various applications.
Composition: Comprises a closed-cell foam formed by a reaction of isocyanate and polyol.
R-Value: Exhibits a high R-value, providing effective thermal insulation.
Environmental Impact: Consideration for environmental impact due to chemical composition.
Form: Available in rigid foam board form, suitable for diverse installations.
Schedule Your Insulation Installation Today!
Conclusion
So, these are the best list of thermal insulation materials that keeping your house warm. You must consider choosing one of them that can suit the best to your needs. One thing to note is that while insulating your home, you must get an R-value recommendation from the Department of Energy in your area. Neo Thermal Insulation is always a perfect choice when it comes to buying insulation materials and providing thermal insulation services. So, these are some of the best insulation materials available to keep your house warm. Choosing the right insulation is crucial to ensure optimal thermal performance and energy efficiency for your home. Before making a decision, it’s advisable to obtain an R-value recommendation from the Department of Energy in your area. The R-value is a measure of thermal resistance, helping you determine the insulation’s effectiveness in preventing heat transfer.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are Insulation Materials?
Insulation materials play a crucial role in thermal insulation, aiming to minimize heat transfer between objects. Heat transfer poses challenges across various industries when objects in contact have disparate temperatures.
2. In the list of thermal insulation materials which is commonly used for insulation?
Loose-fill insulation commonly utilizes materials such as cellulose, fiberglass, and mineral wool (rock or slag). Notably, these materials are crafted from recycled waste products. Cellulose, for instance, is primarily derived from recycled newsprint, while the majority of fiberglass products incorporate 40% to 60% recycled glass.
3. Why should we use insulation material?
Ensuring a consistent temperature throughout the year, insulation safeguards your home from winter cold and summer heat. It also proves effective in diminishing noise disturbances. A properly insulated house exhibits high energy efficiency, requiring minimal additional heating and cooling.
4. Where do we use insulation materials?
Insulation serves as the protective layer you can install on your home’s roof, ceiling, external walls, and floor, mitigating the impact of external temperatures on indoor comfort. This results in a reduced need for energy to heat and cool your home, making it more economical to maintain throughout the entire year.